
In this article, we learn: On media planning in theory: I will give definitions, I will describe the stages, I will share textbooks. On media planning earlier and now: TV, newspapers, radio, outdoor and its highness the Internet. The main indicators of the effectiveness of an advertising campaign on the Internet. How to do real calculations in an Excel table.
Step 1. Data collection
You can order teasers on websites or articles on the forums.
You can order posts in communities with your target audience or launch a viral video before a video on Youtube.
You can order PPC Campaigns in Google or Bing or order WhatsApp-newsletter.
All of these are directly related to your product (service) and your target audience.
For effective advertising media mix we should use the results of the analysis of the brand and entire market.
Our priorities are maximum coverage of target audience and maximum conversion.
2) Choose the secondary advertising channels
A) understand its effectiveness;
B) estimate the deviations and make corrections before the next advertising campaign.
I propose to consider the key performance indicators of an advertising campaign. The first classical indicators are:
CPT = ($5,000 / 3,000,000) x 1,000 = $1.66
3. Cost per click
Media Planning for an Online Advertising Campaign
Every businessman agrees that only properly planned advertising works good.
So do you if you are reading this article.
In this article, we learn:
- On media planning in theory: I will give definitions, I will describe the stages, I will share textbooks.
- On media planning earlier and now: TV, newspapers, radio, outdoor and its highness the Internet.
- The main indicators of the effectiveness of an advertising campaign on the Internet.
- How to do real calculations in an Excel table.
Let’s go.
One of the key processes of a successful advertising campaign is media planning.
Media planning is the process of choosing channels for advertising (placement), the purpose of which is to maximize the effectiveness of an advertising campaign.
The result of this work is a media plan - a document (table, file, presentation) which contains a plan of promotional activities.
Media plan makes it more efficient:
Media planning is the process of choosing channels for advertising (placement), the purpose of which is to maximize the effectiveness of an advertising campaign.
The result of this work is a media plan - a document (table, file, presentation) which contains a plan of promotional activities.
Media plan makes it more efficient:
- Choosing an advertising goal.
- Defining advertising costs.
- Scheduling workload timing of your employees.
- Developing our brand.
We will return later to what the media plan contains. First, any self-respecting company should research the market. INTERVOLGARU does it for any customer.
As you know, media planning is strategic (3-5 years of temporary planning), tactical (1-3 years) and operational (7-120 days). Regardless of time limits, the media plan itself includes 5 basic components:
As you know, media planning is strategic (3-5 years of temporary planning), tactical (1-3 years) and operational (7-120 days). Regardless of time limits, the media plan itself includes 5 basic components:
- Collection of basic, fundamental data.
- Definition of goals.
- Identifying target markets.
- Working with various media, determining their ratio.
- General conclusions on the work.
Step 1. Data collection
Data collection is information about our brand: how our consumer perceives us, what piece of pie we have on the market (our brand’s volume of sales in relation to total sales on the market) and what is the structure of this market, i.e. who are our competitors. And, of course, the portrait of our consumer (hello, sociology!).
For example, recently a regional vegetable-growing company, Botanica, appeared in a neighbouring town Volzhsky. So far, Poland, Turkey and Krasnodar have been operating on the market, as well as a part of the Caucasian suppliers. Accordingly, the company determines the volume of its sales and explores its competitors (suppliers, sales channels, etc.).
With the help of supervisors, it checks brand attitudes at points of sale.
Step 2. Definition of the communication objectives for strategy goals achievementFor example, recently a regional vegetable-growing company, Botanica, appeared in a neighbouring town Volzhsky. So far, Poland, Turkey and Krasnodar have been operating on the market, as well as a part of the Caucasian suppliers. Accordingly, the company determines the volume of its sales and explores its competitors (suppliers, sales channels, etc.).
With the help of supervisors, it checks brand attitudes at points of sale.
Setting goals is the first step to planning advertising communications. Ideally, your brand should have a strategy. This is how the process should be organized. Look at the strategic media planning for Coca-Cola and agree: they are good. So many related commercials, all the slogans are effective in each situation, and some for years to come!
Strategy is possible when your business has goals, your marketing department (or a brave marketer) has goals, your communications (any banner, a radio clip in the morning, a leaflet at the metro) have a goal. Such renowned classic marketing authors F. Kotler and emphasize the importance of goal setting prior to budget planning, not to mention advertising process observing.
Regardless of the communication channel, you must formulate a goal.
For example, increase the number of registrations on landing page by 20% via advertising”.
Or "Through advertising, increase sales in the next quarter by 30%."
And here 3 key point to keep in mind: Strategy, Tactics and “Here and Now”. Make your strategic goal form a tactical one and the actical goal form the communication steps. And then you will not have “The sales figures plummeted in October, because the banners hadn’t been working!”
For example, a company aims at 20% of the market share and a profit level of at least $10,000 per month. To do this, the company has to expand the consumer base from 500 people to 1,000. With advertising on social networks and targeted promotional videos, the company increases brand loyalty. The company also increases the product awareness via the contextual and targeted advertising on promotions and discounts on Google.com and its advertising partners via Google ads.
After buying at a discount consumers are captured by the company in order to organise the targeted email campaign with additional discounts.
Step 3. Identify target markets Strategy is possible when your business has goals, your marketing department (or a brave marketer) has goals, your communications (any banner, a radio clip in the morning, a leaflet at the metro) have a goal. Such renowned classic marketing authors F. Kotler and emphasize the importance of goal setting prior to budget planning, not to mention advertising process observing.
Regardless of the communication channel, you must formulate a goal.
For example, increase the number of registrations on landing page by 20% via advertising”.
Or "Through advertising, increase sales in the next quarter by 30%."
And here 3 key point to keep in mind: Strategy, Tactics and “Here and Now”. Make your strategic goal form a tactical one and the actical goal form the communication steps. And then you will not have “The sales figures plummeted in October, because the banners hadn’t been working!”
For example, a company aims at 20% of the market share and a profit level of at least $10,000 per month. To do this, the company has to expand the consumer base from 500 people to 1,000. With advertising on social networks and targeted promotional videos, the company increases brand loyalty. The company also increases the product awareness via the contextual and targeted advertising on promotions and discounts on Google.com and its advertising partners via Google ads.
After buying at a discount consumers are captured by the company in order to organise the targeted email campaign with additional discounts.
You are aware of how to determine the target audience. It’s more important to know which market segments your target audience is hiding in and how to reach it with our ads?
Step 4 . Working with various media, determining their proportion in the budget
The milestone is a media mix.
Media mix a plan for the integrated use of various advertising channels to effectively fulfill the purpose of an advertising campaign. There are 3 points in creating a good media mix.
1) Choose the main channelsMedia mix a plan for the integrated use of various advertising channels to effectively fulfill the purpose of an advertising campaign. There are 3 points in creating a good media mix.
This stage is directly related to paragraph 3 above.
- Who is your target audience?
- Car owners aged 20-25.
- Great, you on the radio "Young driver"
The classical media planning included three main channels of advertising: TV, radio and print media. However, the online advertising market over the past years has grown to a huge cash flow.
As eMarketer said in 2019, worldwide digital ad spending will rise by 17.6% to $333.25 billion.
According to the eMarketer in some countries digital has already become the dominant ad medium.
- Who is your target audience?
- Car owners aged 20-25.
- Great, you on the radio "Young driver"
The classical media planning included three main channels of advertising: TV, radio and print media. However, the online advertising market over the past years has grown to a huge cash flow.
As eMarketer said in 2019, worldwide digital ad spending will rise by 17.6% to $333.25 billion.
According to the eMarketer in some countries digital has already become the dominant ad medium.
And we are happy to start writing only about online advertising – because we specialize in it.
You should strictly divide advertising into 5 large segments:
You should strictly divide advertising into 5 large segments:
- PPC campaigns;
- display advertising;
- video ads;
- publications on social networks, blogs and news websites, working with influencers;
- email campaigns.
You can order teasers on websites or articles on the forums.
You can order posts in communities with your target audience or launch a viral video before a video on Youtube.
You can order PPC Campaigns in Google or Bing or order WhatsApp-newsletter.
All of these are directly related to your product (service) and your target audience.
For effective advertising media mix we should use the results of the analysis of the brand and entire market.
Our priorities are maximum coverage of target audience and maximum conversion.
2) Choose the secondary advertising channels
Your target audience might not be precisely determined, and you might not know its portrait.
Therefore, spending a part of the budget on secondary advertising channels allows it to be determined.
3) Final media mix and ordering advertisement
Therefore, spending a part of the budget on secondary advertising channels allows it to be determined.
You combined the results of stage 1 and stage 2, eliminated unnecessary placements and ordered an advertising campaign. Hooray!
Step 5. Analysis of the results
It is necessary to analyze the past ad campaign correctly in order to: Step 5. Analysis of the results
A) understand its effectiveness;
B) estimate the deviations and make corrections before the next advertising campaign.
I propose to consider the key performance indicators of an advertising campaign. The first classical indicators are:
- Profitability of an advertising campaign.
- Price per thousand contacts.
- Cost per click.
- Click through rate.
- Lead cost.
- Number of new consumers.
- Average check size.
1. Profitability of an advertising campaign
ROMM = (Profit from product sales after advertising campaign / advertising costs) х 100%.
ROMM – Return On Marketing Margin.
It is important to correctly track the impact of adver tising on the sale of goods. To track the offline sales influence use the new product packaging, and the easiest is the new price for the product.
It is important to correctly track the impact of adver tising on the sale of goods. To track the offline sales influence use the new product packaging, and the easiest is the new price for the product.
For example: in the previous quarter, you carried out a media advertising and as a result sold goods for $70,000. You spent
$5,000 for a 3-month period.
ROMM = ($70,000 / $5,000) х 100% = 1,400 % (super!)
$5,000 for a 3-month period.
ROMM = ($70,000 / $5,000) х 100% = 1,400 % (super!)
2. Price per thousand contacts
CPT, Cost per Thousand — the cost of 1,000 contacts with the audience, readers or viewers. We still do not know the audience’s attitude to the product. They are our potential consumers.
For example: you spent $5,000 on targeted advertisements on Facebook and reached 3,000,000 people.
For example: you spent $5,000 on targeted advertisements on Facebook and reached 3,000,000 people.
CPT = ($5,000 / 3,000,000) x 1,000 = $1.66
3. Cost per click
Cost per Click (CPC) shows the cost per click of an interested user.
CPT is used to determine the cost of coverage, and CPC is used to determine the cost per click of a potential buyer.
CPT is used to determine the cost of coverage, and CPC is used to determine the cost per click of a potential buyer.
CPC = advertising campaign budget / number of clicks.
For example, you spent on advertising in Google Ads $2,500 per quarter and received 800 clicks on your site.
CPC = $2,500 / 800 = $3.125 (expensive, of course!)
For example, you spent on advertising in Google Ads $2,500 per quarter and received 800 clicks on your site.
CPC = $2,500 / 800 = $3.125 (expensive, of course!)
4. Click through rate
CTR (click-through rate) shows how many your ad impressions were there and how many people clicked on it.
It very useful to determine if “this damned ad” works or not.
CTR = number of clicks on advertising / number of ad impressions * 100%.
For example, you launched a media campaign on Youtube. Three ads were showed 10,000 times, and there were 900 clicks on them.
CTR = 900 / 10 000 * 100% = 0,09% (too small to talk about good advertising, the best CTR for video ads is about 1%).
It very useful to determine if “this damned ad” works or not.
CTR = number of clicks on advertising / number of ad impressions * 100%.
For example, you launched a media campaign on Youtube. Three ads were showed 10,000 times, and there were 900 clicks on them.
CTR = 900 / 10 000 * 100% = 0,09% (too small to talk about good advertising, the best CTR for video ads is about 1%).
5. Lead cost
Lead is not a promotional contact, but people interested in your product (service). Here we do not expect clicks, but work with real people.
For example, if you do not have an online store, then going to the website does not guarantee a purchase or order.
A visit could result in a call or request.
In general, leads are most often considered when selling services.
The cost of attracting the lead (Cost Per Lead) is calculated easily.
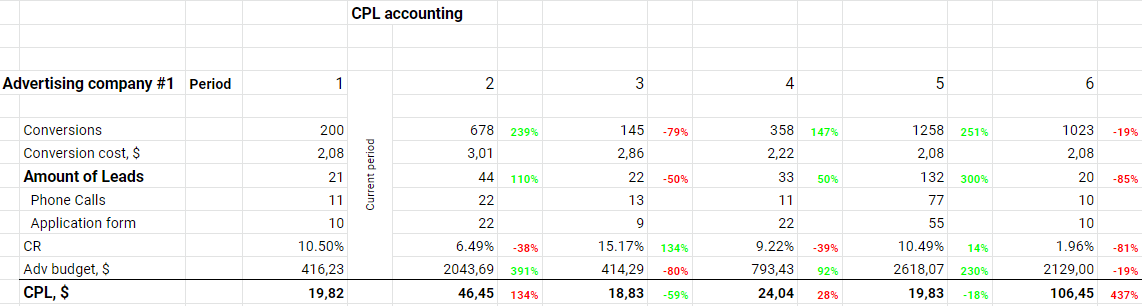
CPL = advertising campaign budget / number of leads.
Analyze CPL for quarters and periods to understand which of your actions help to increase the number of leads and subsequent sales. We have prepared for you a table with calculations.
A visit could result in a call or request.
In general, leads are most often considered when selling services.
The cost of attracting the lead (Cost Per Lead) is calculated easily.
CPL = advertising campaign budget / number of leads.
P.S. The cost of a lead only includes marketing and advertising expenses but not salaries or operating costs.
6. Number of new customers
The number of new customers is very important because it works for the future sales of a company.
Even a small number of new people in your contact database will enable you to sell more in the future.
7. Average order value
It is relevant when you have several target groups in your advertising campaign. You will be able to determine the average check for different target groups, i.g. $25-30 for teacher and $30-35 for programmer.
We create effective advertising media plans. We carefully analyze the results and draw conclusions. Call INTERVOLGARU and we make audit of your advertising campaign.
We create effective advertising media plans. We carefully analyze the results and draw conclusions. Call INTERVOLGARU and we make audit of your advertising campaign.
For additional examples, please email: info@intervolgaru.com
- 02.05.2019
-
Viktor Stavitskiy
